
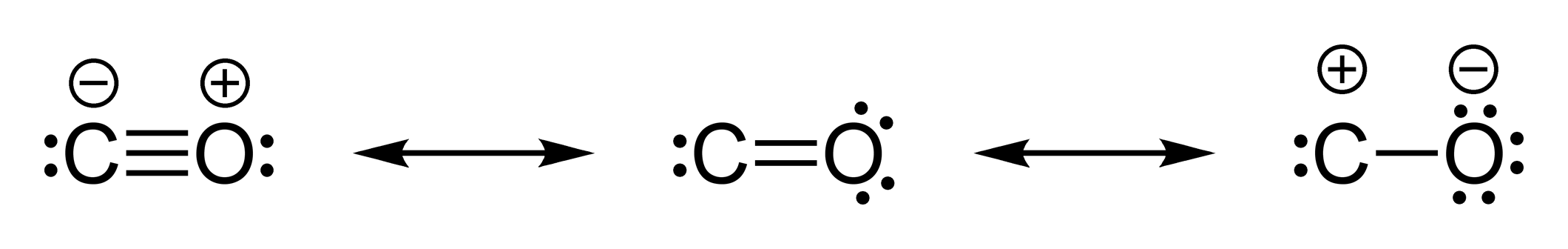
Subtract this number from the total number of valence electrons in benzene and then locate the remaining electrons such that each atom in the structure reaches an octet. or q), in the covalent view of chemical bonding, is the hypothetical charge assigned to an atom in a molecule.Then calculate the number of valence electrons used in this drawing. Draw a circle around the atom for which a formal charge is desired (similar to carbon dioxide below). Draw a structure for benzene illustrating the bonded atoms.Given: molecular formula and molecular geometry Use resonance structures to describe the bonding in benzene. It does not fluctuate between resonance forms rather, the actual electronic structure is always the average of that shown by all resonance forms.\)) consists of a regular hexagon of carbon atoms, each of which is also bonded to a hydrogen atom. In each of them, the formal charge on the center carbon is 0, the double bonded oxygen is 0, and the two single bonded oxygens are each -1. In this case, the sum of the formal charges is 0 + 1 + 0 + 0 + 0 +1. Adding together the formal charges on the atoms should give us the total charge on the molecule or ion. The formal charges on the atoms in the NH 4+ ion are thus. All atoms in BrCl 3 have a formal charge of zero, and the sum of the formal charges totals zero, as it must in a neutral molecule. The formal charge on each hydrogen atom is therefore. Bonding Patterns For organic chemistry, the common bonding patterns of carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen have useful applications when evaluating chemical structures and reactivity. In other words, carbon is tetravalent, meaning that it commonly forms four bonds. And each carbon atom has a formal charge of zero. In the structures of methane, methanol, ethane, ethene, and ethyne, there are four bonds to the carbon atom.
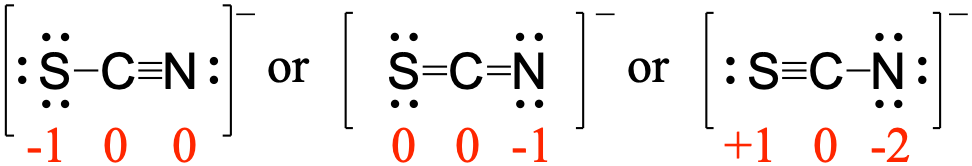
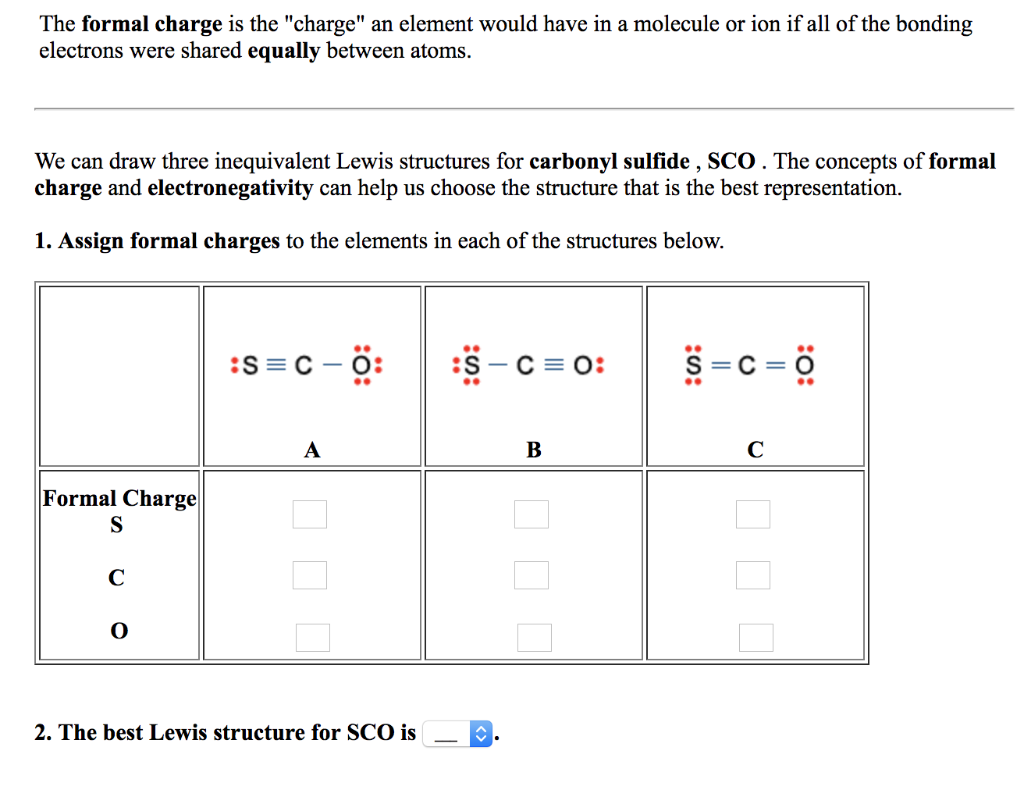
If the number of assigned electrons is greater than the Group.

We should remember that a molecule described as a resonance hybrid never possesses an electronic structure described by either resonance form. Subtract this number from the number of valence electrons for the neutral atom. Carbon, the most important element for organic chemists. If the number of assigned electrons is equal to the Group Number, then Formal Charge is zero (0). However, the sum of the formal charges of these atoms equals the net charge of the species, which in this case is zero. Formal charge can also be applied to simple molecules and. Brackets surround this structure, and there is a superscripted negative sign. The formal charge of carbon is 1 and the formal charge of nitrogen is + 1. The preferred Lewis structure of a molecule is that in which the formal charges are closest to zero. The right structure shows an oxygen atom with three lone pairs of electrons single bonded to a nitrogen atom with one lone pair of electrons that is double bonded to an oxygen atom with two lone pairs of electrons. Formal Charge of H (1 valence e-) - (0 lone pair e-) - (1/2 x 2 bond pair e-) 0. The formal charge on each hydrogen atom is therefore. Carbon monoxide has a structure that is very similar to formaldehyde.
Brackets surround this structure, and there is a superscripted negative sign. Each hydrogen atom in has one bond and zero non-bonding electrons. There are no formal charges on the hydrogens either. The left structure shows an oxygen atom with two lone pairs of electrons double bonded to a nitrogen atom with one lone pair of electrons that is single bonded to an oxygen atom with three lone pairs of electrons. Two Lewis structures are shown with a double headed arrow drawn between them.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
